Post jest kontynuacją 3-ciej części serii.
W dzisiejszym poście zajmiemy się webscrapingiem stron www. Dzięki tej technice, oprócz przyjmowania czystego tekstu, nasz RAG będzie potrafił samodzielne pobierać informacje bezpośrednio z stron internetowych.
Czyszczenie danych
Na samym początku tworzymy naszą metodę która będzie pobierała treść strony www, następnie usuwała z niej wszelkie style i skrypty. Pozwoli to nam zaoszczędzić tokeny i pozbyć się całkowicie zbędnego tekstu.
def fetch_url_text(url: str) -> str:
try:
r = requests.get(url, timeout=10)
r.raise_for_status()
except Exception as e:
print(f"Nie udało się pobrać {url}: {e}")
return ""
soup = BeautifulSoup(r.text, "html.parser")
for s in soup(["script", "style", "noscript", "iframe"]):
s.extract()
text = soup.get_text(separator=" ")
text = " ".join(text.split())
return text
Aby nasza funkcja, potrafiła przyjmować większą ilość adresów url. Dodamy do niej wrapper który przyjmie ich listę i dla każdego wywoła powyższą funkcję.
def load_data_from_url(urls: List[str]) -> List[Dict]:
data = []
for idx, url in enumerate(urls):
page_body = fetch_url_text(url)
if page_body:
data.append(
{
"id": f"doc-{idx}-{url.replace('https://', '').replace('/', '_')}",
"doc": page_body,
"meta": {"source": url},
}
)
return data
Z racji że w 1-szej części dodaliśmy metodę load_sample_data(), włożymy ją w funkcję opakowującą. W przypadku braku podania listy adresów url, zwróci nam ona przykładowe dane. W przeciwnym razie otrzymamy nam treść pobranych stron.
def load_docs(urls: Optional[List[str]] = None) -> List[Dict]:
if urls:
return load_data_from_url(urls)
return load_sample_data()
Pełny kod:
import json
from typing import Dict, List, Optional
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
from rich.console import Console
from rich.panel import Panel
from rich.table import Table
def fetch_url_text(url: str) -> str:
"""
Fetches the page content from the provided URL and extracts plain text.
Args:
url (str): The URL of the page to fetch.
Returns:
str: The plain text content of the page, or an empty string if the content could not be retrieved.
"""
try:
r = requests.get(url, timeout=10)
r.raise_for_status()
except Exception as e:
print(f"Nie udało się pobrać {url}: {e}")
return ""
soup = BeautifulSoup(r.text, "html.parser")
for s in soup(["script", "style", "noscript", "iframe"]):
s.extract()
text = soup.get_text(separator=" ")
text = " ".join(text.split())
return text
def load_data_from_url(urls: List[str]) -> List[Dict]:
"""
Fetches the content of pages from the provided list of URLs and returns a list of dictionaries in the following format:
[{"id": ..., "doc": ..., "meta": {"source": ...}}, ...]
Args:
urls (List[str]): A list of URLs to fetch content from.
Returns:
List[Dict]: A list of dictionaries where each dictionary contains the following keys:
- "id": A unique identifier for the document (e.g., a combination of URL and index).
- "doc": The plain text content fetched from the URL.
- "meta": A dictionary with metadata, including the "source" key that stores the URL.
Example:
[
{"id": "doc-0-example_com", "doc": "Page content", "meta": {"source": "http://example.com"}},
{"id": "doc-1-example_org", "doc": "Another page content", "meta": {"source": "http://example.org"}}
]
"""
data = []
for idx, url in enumerate(urls):
page_body = fetch_url_text(url)
if page_body:
data.append(
{
"id": f"doc-{idx}-{url.replace('https://', '').replace('/', '_')}",
"doc": page_body,
"meta": {"source": url},
}
)
return data
def load_sample_data() -> List[Dict]:
"""
Returns sample data in JSON format.
This method provides a predefined set of sample documents, each containing an identifier (`id`),
text content (`doc`), and metadata (`meta`) with the source of the document.
Returns:
List[Dict]: A list of dictionaries, each representing a sample document with the following keys:
- "id": A unique identifier for the document.
- "doc": The content of the document as a string.
- "meta": A dictionary with metadata about the document, including the "source" key.
Example:
[
{"id": "doc1", "doc": "Chroma is an engine for vector databases.", "meta": {"source": "notes"}},
{"id": "doc2", "doc": "OpenAI embeddings allow text to be converted into vectors.", "meta": {"source": "blog"}}
]
"""
json_data = """
[
{"id":"doc1", "doc":"Chroma is an engine for vector databases.", "meta":{"source":"notes"}},
{"id":"doc2", "doc":"OpenAI embeddings allow text to be converted into vectors.", "meta":{"source":"blog"}},
{"id":"doc3", "doc":"LangChain makes it easier to create applications based on LLMs.", "meta":{"source":"documentation"}},
{"id":"doc4", "doc":"Vector databases enable efficient searching through large text data sets.", "meta":{"source":"article"}},
{"id":"doc5", "doc":"RAG combines text generation with real-time information retrieval.", "meta":{"source":"presentation"}}
]
"""
return json.loads(json_data)
def load_docs(urls: Optional[List[str]] = None) -> List[Dict]:
"""
Loads documents. If URLs are provided, fetches their content; otherwise, returns sample data.
If a list of URLs is provided, this method will attempt to fetch the content from each URL and return it in the
form of a list of dictionaries. If no URLs are provided, it will return a predefined set of sample data.
Args:
urls (Optional[List[str]], optional): A list of URLs to fetch content from. Defaults to None.
Returns:
List[Dict]: A list of dictionaries, where each dictionary contains the following:
- "id": A unique identifier for the document.
- "doc": The content of the document (text from the URL or sample data).
- "meta": A dictionary with metadata about the document, including the "source" key with the URL or source of sample data.
Example:
If URLs are provided:
[
{"id": "doc-0-example_com", "doc": "Page content", "meta": {"source": "http://example.com"}},
{"id": "doc-1-example_org", "doc": "Another page content", "meta": {"source": "http://example.org"}}
]
If no URLs are provided, returns sample data:
[
{"id": "doc1", "doc": "Chroma is an engine for vector databases.", "meta": {"source": "notes"}},
{"id": "doc2", "doc": "OpenAI embeddings allow text to be converted into vectors.", "meta": {"source": "blog"}}
]
"""
if urls:
return load_data_from_url(urls)
return load_sample_data()
docs = ["https://kamdev.pl", "http://blog.kamdev.pl"]
data = load_docs(docs)
# Wyświetlenie pobranych danych
console = Console()
table = Table(title="Zaimportowane strony", show_lines=True)
table.add_column("ID")
table.add_column("Body")
table.add_column("Tytuł")
for doc in data:
table.add_row(doc["id"], doc["doc"][:80], doc["meta"].get("source", "brak źródła") )
console.print(table)
Po uruchomieniu powyższego programu otrzymujemy:
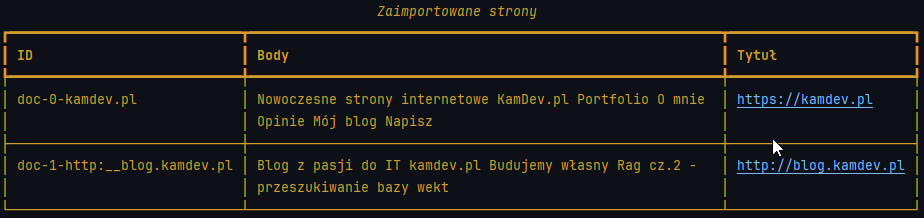
*Kolumna body została celowo skrócona dla zachowania czytelności.


Komentarze